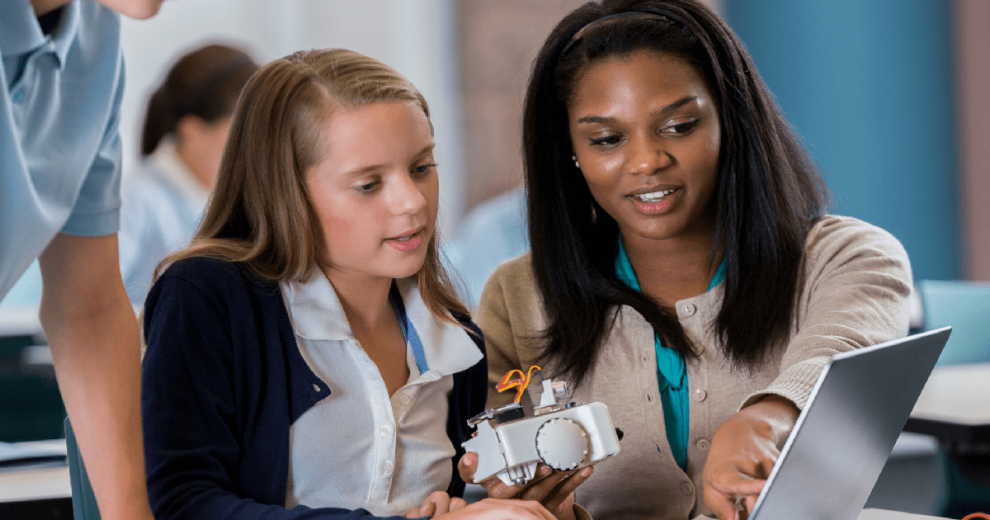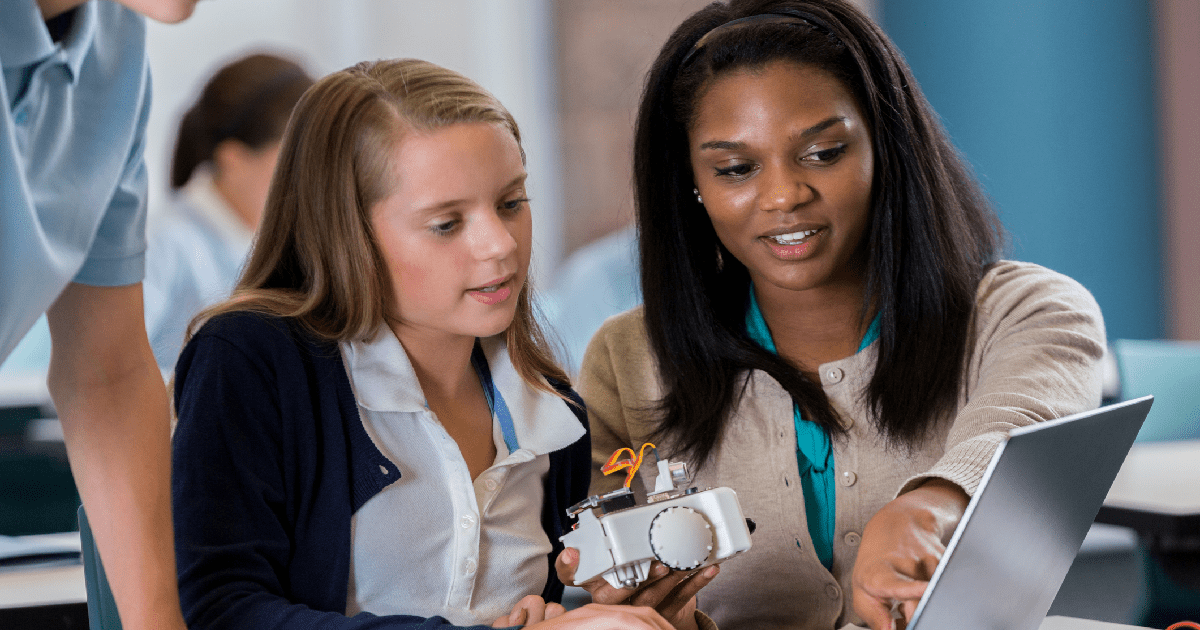
Introduction
Mentorship plays a vital role in the development and success of individuals in various fields, and this is particularly true in the realm of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). Mentors provide guidance, support, and inspiration to aspiring scientists, engineers, mathematicians, and technologists, helping them navigate challenges and achieve their goals. In this article, we will explore the significant role mentors play in STEM fields, incorporating the latest technologies, real-life examples, and quotes from influential figures.
- Guidance and Support in Career Exploration
One of the primary roles of mentors in STEM is to guide and support individuals in their career exploration journey. Mentors can provide valuable insights and advice on various STEM disciplines, helping mentees make informed decisions about their educational paths and future careers. Consider the following aspects of mentorship in career exploration:
1.1 Sharing Personal Experiences
Mentors share their own experiences, challenges, and successes in their STEM careers. By providing firsthand accounts, mentors give mentees a glimpse into the realities of working in different STEM fields, helping them understand the possibilities and requirements of each career path.
1.2 Exploring STEM Opportunities
Mentors help mentees explore diverse opportunities within the STEM landscape. They can provide information about internships, research programs, conferences, and other avenues for gaining practical experience and exposure to the field. Mentors help mentees identify and seize opportunities that align with their interests and aspirations.
1.3 Offering Insightful Advice
Mentors provide advice on navigating educational choices, selecting courses, pursuing advanced degrees, and finding career opportunities. Their guidance is instrumental in helping mentees make informed decisions that align with their passions, strengths, and long-term goals.
- Building Skills and Fostering Personal Development
Mentors play a crucial role in building essential skills and fostering personal development in aspiring STEM professionals. They provide guidance on developing technical skills, cultivating professional attributes, and nurturing a growth mindset. Consider the following aspects of mentorship in skill building and personal development:
2.1 Technical Skill Development
Mentors assist mentees in developing technical skills relevant to their chosen STEM fields. Whether it’s programming, lab techniques, or engineering design, mentors provide guidance, resources, and feedback to help mentees acquire and refine these skills.
2.2 Professional Networking
Mentors help mentees build professional networks within the STEM community. They provide introductions, connect mentees with experts and industry professionals, and facilitate opportunities for mentees to engage with like-minded individuals in their field of interest.
2.3 Nurturing a Growth Mindset
Mentors foster a growth mindset in mentees, encouraging them to embrace challenges, persevere through setbacks, and view failure as an opportunity for learning and growth. They instill confidence and resilience, helping mentees navigate obstacles and develop a positive attitude toward continuous improvement.
- Providing Emotional Support and Encouragement
In addition to providing guidance and skill development, mentors offer invaluable emotional support and encouragement to mentees. The mentor-mentee relationship can serve as a source of motivation, inspiration, and reassurance during challenging times. Consider the following aspects of mentorship in emotional support:
3.1 Offering Encouragement and Motivation
Mentors provide encouragement and motivation to mentees, especially when they face self-doubt or encounter obstacles in their STEM journeys. They share words of wisdom, inspire confidence, and remind mentees of their potential and the value they bring to the field.
3.2 Creating a Supportive Environment
Mentors create a safe and supportive environment where mentees can openly discuss their challenges, concerns, and aspirations. They listen attentively, provide empathy, and offer constructive feedback, fostering a sense of trust and belonging.
3.3 Advocating for Mentees
Mentors act as advocates for mentees, promoting their achievements, skills, and potential within their professional networks. They help mentees overcome barriers, navigate biases, and create opportunities for mentees to showcase their talents and contributions.
Conclusion
Mentors play a critical role in shaping the next generation of STEM professionals. Through guidance, support, skill development, and emotional encouragement, mentors empower mentees to pursue their passions, overcome challenges, and achieve success in STEM fields. As Maya Angelou once said, “I’ve learned that you shouldn’t go through life with a catcher’s mitt on both hands. You need to be able to throw something back.” Let us embrace the power of mentorship in STEM and ensure that aspiring scientists, engineers, mathematicians, and technologists receive the guidance they need to excel and make their mark in the world.

















